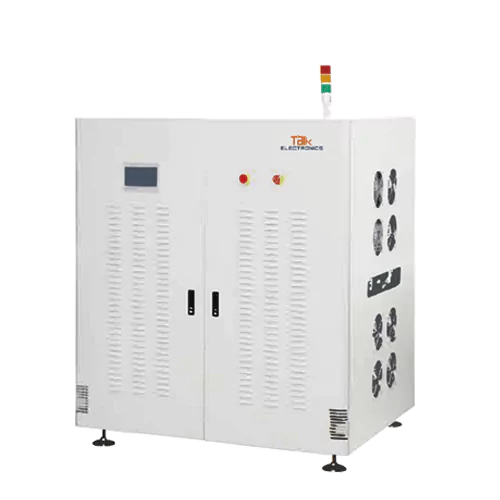
BF-350C Cooling Buffer
Feature
Smooth transmission of heavy PCBs.
Three operation modes: FIFO, LIFO, By-pass
Fast cooling effect: decreasing the temperature of PCB boards quickly
Adopt side storage of board to enhance cooling function and increase the number of storage.
Customization is always available, please mark down your need when contact us.
What is a cooling buffer?
A cooling buffer is an engineered staging system designed to temporarily hold parts, components or materials between manufacturing processes to allow controlled cooling before further handling or processing.
The importance of cooling buffers in modern manufacturing
Regulated cooling enabled by buffers prevents defects like warping in parts. Gradual cooling also optimizes process throughput versus sudden cooling. Cooling buffers are vital for quality and efficiency.
Types of cooling buffers
Air-cooled buffers:
Use air circulation to dissipate heat from parts in the buffer. Simple and economical.
Liquid-cooled buffers:
Use liquid mediums like water or oil for cooling. Better heat transfer.
Hybrid buffers:
Combine air and liquid cooling to balance effectiveness and operating costs.
Cooling mediums
Air:
Air cooling is simple and low cost but slower at heat removal.
Water:
Water circulated in jackets or immersion tanks provides high heat transfer rates.
Oil:
Oils are used for consistency in cooling and suitability for food contact.
Benefits of Using Cooling Buffers
Preventing overheating and damage to sensitive components
Controlled cooling prevents warpage, distortion and damage to parts like plastics or electronics.
Improved product quality and consistency
Gradual, consistent cooling minimizes defects and results in repeatable output quality.
Enhanced production throughput and reduced downtime
Immediate downstream processing without waiting for batches to cool avoids work-in-progress buildup.
Environmental sustainability and energy efficiency
Enclosed cooling buffers allow heat recovery and reuse, reducing energy consumption.
Key Features of Cooling Buffers
Cooling medium selection and design considerations
Type, temperature and circulation of cooling medium depends on part material, size and target cooling rate.
Buffer size and capacity for specific cooling requirements
Inventory capacity, dwell time and throughput are factored based on production volumes and cycle times.
Integration with other manufacturing equipment
Adapters or conveyors enable seamless transfer of parts from upstream and downstream equipment.
Control and monitoring systems for temperature regulation
PLC-based controls precisely regulate cooling medium flow, temperature and dwell times based on feedback.
Industries and Applications
Electronics and semiconductor manufacturing
Controlled cooling of dies prevents thermal shocks and enables efficient processing.
Metal fabrication and welding processes
Gradual cooling of welded metal parts avoids cracks and maintains desired metallurgical properties.
Plastic molding and extrusion industries
Cooling buffers allow molded or extruded plastic parts to completely cure without deformities.
Choosing the Right Cooling Buffer
Evaluating specific cooling needs and heat dissipation requirements
Part material, size, target cooling rate, acceptable temperature ranges etc. guide requirements.
Considering buffer size and cooling capacity
Inventory space, dwell times, cooling medium flow rates etc. are optimized based on production throughput.
Customization options for unique manufacturing needs
Custom buffer dimensions, number of cooling stages or chambers, conveyor types and accessory integration is possible.
Cost-effectiveness and return on investment considerations
While cooling buffers involve higher initial costs, the downstream process benefits justify the investment.
Installation and Maintenance
Pre-installation preparations and site evaluation
Installation site is assessed for utilities like water supply, drainage, compressed air and sufficient clearances.
Proper integration of cooling buffers into the production line
Experienced technicians ensure optimal integration, buffer sequencing, controls logic and trial runs.
Routine maintenance to ensure optimal performance
Consumables replenishment, leak checks, pump/compressor servicing, filter cleaning form routine maintenance.
Troubleshooting common issues and solutions
Temperature deviations, fluid leaks, conveyor jams and sensor failures are promptly diagnosed and addressed.
Comparing Cooling Buffers with Traditional Cooling Methods
Air cooling vs. cooling buffers
While air cooling is uncontrolled, buffers allow regulated cooling tailored to part needs.
Advantages of cooling buffers in precise temperature control
Cooling buffers provide fine control over cooling rate impossible with traditional air or batch water cooling.
Liquid cooling and its benefits in heat dissipation
Liquid mediums like water or oil enable rapid, consistent heat removal that air cooling cannot match.
Ensuring Safety and Efficiency
Operator safety measures during cooling buffer operation
Implementing safe material loading/unloading procedures, emergency stops, leak containment and PPE use enhances safety.
Emergency shutdown and safety interlock systems
Interlocks prevent operation unless conditions are safe. Emergency shutdown switches deploy during process upsets.
Environmental impact considerations and waste management
Measures like fluid recycling, responsible disposal, transitioning to greener coolants and preventing leaks safeguard sustainability.
Specification of BF-350C Cooling Buffer
| Description | Cooling buffer used after oven or before AOI |
|---|---|
| Cycle time | Approx. 10seconds |
| Maximum PCBs capacity | 20pcs (support customization) |
| Power supply | AC 110/220 volts; single phase |
| Power | Max. 300VA |
| Transport height | 900 +/- 20mm (support customization) |
| Transport direction | L to R/R to L |
Dimension of BF-350C Cooling Buffer
| Model | Dimension (LxWxH, mm) | PCB board size (LxWxH, mm) | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BF-350C | 1500*1495*1760 | 150*150-1200*350 | 300 |
Conclusion
Recap of the significance of cooling buffers in modern manufacturing
Cooling buffers enable vital controlled cooling of parts and materials between temperature-sensitive manufacturing processes, preventing defects and enabling lean, efficient workflows.
Emphasizing their role in enhancing heat dissipation and production efficiency
By filling a critical process need, cooling buffers are indispensable for quality and productivity in various industries from plastics to electronics manufacturing.
Encouraging industries to adopt cooling buffers for improved product quality and energy-efficient manufacturing processes
The substantial benefits make integrating cooling buffers an important consideration for manufacturers aiming for product excellence, responsible energy usage and streamlined, defect-free processing.
F.A.Qs
Adjustable temperature controls, variable speeds and modular buffer design enable reconfiguration to meet revised needs.
Key factors are cooling medium, flow rate, temperature difference, dwell time and contact intimacy with parts.
Immediate downstream processing without waiting for batches to cool avoids work-in-progress accumulation and smoothens flow.
Yes, cooling buffers can interface with upstream/downstream processes via adapters and workpiece transfer systems.
Routine daily, weekly and monthly preventive maintenance is scheduled based on usage levels as per OEM recommendations.
Controlled cooling prevents defects like warping or cracking to deliver consistent product quality.
Yes, staff need proper training on safe material handling, equipment operation, PPE use and maintenance basics.
Typical uses include cooling extruded plastics, molds, welded fabrications, semiconductor components etc. before next stage.
Yes, liquid-cooled buffers can effectively dissipate heat from parts exiting high temperature processes like heat treatment.
Consistent contact with cooling medium unlike batch cooling allows rapid, uniform heat removal from parts.
Solving the PCBA industry biggest problems
Working with ElectronicsTalk offers you high-standard PCBA products that are supplied from credible manufacturers in attractive cost.
We dedicate to provide the best customer support, its the vital aspect of our company philosophy.
Contact Your PCBA Experts By One Click
We help you avoid the pitfalls to deliver the quality and value of your PCBA solutions, on-time and on-budget.
Contact Your PCBA Experts By One Click
We help you avoid the pitfalls to deliver the quality and value your PCBA solutions, on-time and on-budget.